 Home
Home
April 7, 2023
Subcutaneous Medication Administration at the End of Life
The oral route is by far the most common way medications are administered – even in the hospice setting. However, it’s not always feasible for a number of reasons – dysphagia, nausea/vomiting, or obtundation to name a few.1,2
Administering drugs subcutaneously (SC/SQ) is one method used to overcome patients’ inability to swallow and absorb oral dosage forms.1-4 With SC/SQ administration, parenteral dosage forms are injected under the dermis and epidermis into the subcutaneous tissue, rather than into veins (IV) or muscles (IM).5 Various anatomic sites like the abdomen, thigh, chest, upper arms, or back are suitable for SC/SQ administration.5 Despite its many advantages, there are also potential issues and barriers associated with this route of administration (Table 1).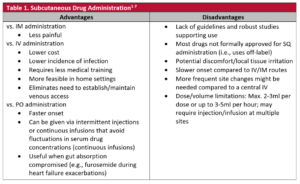
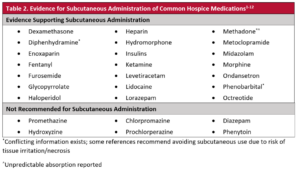
Unfortunately, most drugs aren’t formally authorized for subcutaneous administration and are used off-label.2 As such, questions arise as to which drugs can be given subcutaneously. Table 2 lists medications reported to be acceptable for subcutaneous use as well as those that are unsuitable. Subcutaneous drug administration is one of many tools in the hospice clinician’s symptom management toolbox. As patients decline or become unable to swallow oral dosage forms, alternate routes of medication administration will inevitably become necessary.
Written by: OnePoint Patient Care Clinical Team
Joseph Solien, PharmD, BCGP, BCPP – Vice President of Clinical Services
Melissa Corak, PharmD, BCGP – Senior Clinical Pharmacist
John Corrigan, PharmD, BCGP – Clinical Pharmacist
References
- Bartz L, Klein C, Seifert A, et al. Subcutaneous Administration of Drugs in Palliative Care: Results of a Systematic Observational Study. Journal of Pain and Symptom Management. 2014;48(4):540-546. doi:1016/j.jpainsymman.2013.10.018
- Wernli U, Durr F, Jean-Petit-Matile S, Kobleder A, Meyer-Massetti C. Subcutaneous Drugs and off-label Use in Hospice and Palliative Care: A Scoping Review. Journal of Pain and Symptom Management. 2022;64(5):e250-e259. doi:1016/j.jpainsymman.2022.07.006
- Herndon C, Fike D. Continuous Subcutaneous Infusion Practices of United States Hospices. Journal of Pain and Symptom Management. 2001;22(6):1027-1037 doi:1016/S0996-3924(01)00365-7
- Storey P, Hill Jr. H, St. Louis RH, Tarver E. Subcutaneous Infusions for Control of Cancer Symptoms. Journal of Pain and Symptom Management. 1990;5(1):33-41. doi: 1016/S0885-3924(05)80007-7
- Kestenbaum M, Vilches A, Messersmith S et al. Alternative Routes to Oral Opioid Administration in Palliative care: A Review and Clinical Summary. Pain Medicine. 2014;15:1129-1153. doi:1111/pme.12464
- McPherson ML. Converting Among Routes and Formulations of the Same Opioid. In: Demystifying Opioid Conversion Calculations A Guide for Effective Dosing. 2nd American Society of Health-System Pharmacists; 2018:21-30.
- Lexicomp Online, Lexi-Drugs Online, Hudson, Ohio: Wolters Kluwer Clinical Drug Information, Inc.; 2022.
- Chen A, Loquias E, Roshan R, et al. Safe Use of Subcutaneous Diphenhydramine in the Inpatient Hospice Unit. American Journal of Hospice and Palliative medicine. 2017;34(10):954-957. doi: 1177/1049909116668160
- Weissman D. Fast Facts and Concepts #28 Subcutaneous Opioid Infusions. Palliative Care Network of Wisconsin. 3rd Edition; May 2015. https://www.mypcnow.org/fast-fact/subcutaneous-opioid-infusions/
- Sutherland A, Meldon C, Harrison T, Miller M. Subcutaneous Levetiracetam for the Management of Seizures at the End of Life: An Audit and Update Literature Review. Journal of Palliative Medicine. 2021;24(7):976-981. doi:1089/jpom.2020.0414.
- Kiani CS, Hunt RW. Lidocaine Continuous Subcutaneous Infusion for Neuropathic Pain in Hospice Patients: Safety and Efficacy. Journal of Pain & Palliative Pharmacotherapy. 2021;35(1):52-62. doi: 1080/15360288.2020.1852357
- Richards Hosgood J, Kimbrel J, McCrate B, Grauer p. Evaluation of Subcutaneous Phenobarbital Administration in Hospice Patients. American Journal of Hospice & Palliative Medicine. 2016;33(3):209-213. doi:1177/1049909114555157